No products in the cart.
Dominate the game with Positional Rotations: How to generate them
Football is a dynamic sport that calls for effective collaboration and deliberate movement patterns. Rotations in position rate among the game’s most important components, particularly when positional play is involved. Football positional rotations will be discussed in detail in this piece, along with their importance and how they aid in a team’s success. We’ll cover a wide range of topics in our examination, from basic concepts to sophisticated tactics, so you can fully understand this crucial game mechanic.
Table of Contents
Understanding Positional Rotations
Positional rotations refer to the strategic movement and interchange of players within a team during a match. It involves players switching their positions on the field in an organized and coordinated manner. The primary purpose of positional rotations is to create space, confuse opponents, and exploit opportunities. By rotating positions, players can adapt to different situations, enhance team dynamics, and maintain a fluid style of play.
Let’s take renowned coach Pep Guardiola as an example. Guardiola has successfully stressed positional rotations throughout his coaching career. His teams have proven the advantages of fluid positional play, including FC Barcelona and Manchester City. Players with the skill to switch positions smoothly, such as Lionel Messi and Kevin De Bruyne, can wreck havoc on opposing defenses.
The Benefits of Positional Rotations
Positional rotations offer several advantages to a football team. Let’s explore some of the key benefits:
- Increased Flexibility
By implementing positional rotations, teams can adapt to various formations and strategies more effectively. Players become versatile and can seamlessly fill multiple positions if needed. This flexibility enables teams to respond quickly to changes in the game and counter their opponents’ tactics. It also allows for easier adjustments during injuries or substitutions, ensuring that the team’s performance remains strong.
For example, if a team’s regular left-back is injured, a midfielder can rotate into that position, providing cover and maintaining the team’s defensive structure without compromising their attacking options.
- Improved Attacking Opportunities
Positional rotations create confusion for opposing defenders, as players constantly interchange positions. This unpredictability makes it challenging for defenders to mark specific players and opens up space for attackers to exploit. It allows teams to launch unexpected attacks, catch opponents off guard, and create scoring opportunities. By constantly shifting positions, players can find gaps in the defense and make incisive runs, increasing the team’s chances of scoring goals.
For instance, in a positional rotation, a winger can temporarily swap positions with a forward, creating confusion among the opposition’s defenders. The winger’s movement into a more central position can create space for overlapping fullbacks or midfielders to exploit and deliver crosses into the box.
- Enhanced Team Chemistry
When players rotate positions regularly, they develop a deeper understanding of their teammates’ roles and responsibilities. This improves communication and coordination among players, leading to better teamwork and a more cohesive playing style. Players gain a comprehensive view of the game from different positions, fostering a stronger bond and trust within the team. This unity translates into better on-field performance, as players anticipate each other’s movements and make intelligent decisions based on their shared understanding.
An example of enhanced team chemistry through positional rotations can be seen in Barcelona’s famous tiki-taka style of play. In this system, players constantly rotate positions, maintaining possession and creating passing triangles. This fluidity and understanding between players allow Barcelona to dominate matches and create scoring opportunities
Implementing Positional Rotations
To effectively implement positional rotations, coaches and players must understand the strategic aspects involved. Here are some key considerations:
- Player Skillsets
The best positions for each player should be determined by the coach after evaluating their skills. Each athlete needs to feel at ease and be able to execute in a variety of roles. Coaches can make informed choices on positional rotations by being aware of each player’s strengths and weaknesses. This makes sure that players are used in roles that will allow them to contribute the most to the squad.
For instance, a player with exceptional passing skills and vision might alternate between playing in central midfield and offensive midfield positions since they can help set up goals and manage the pace of the game.
- Tactical Awareness
The strategies and lineups of the squad must be thoroughly understood by the players. They can exploit weaknesses in the opposition’s defense and create scoring opportunities thanks to this knowledge, which also enables them to modify their positioning in accordance with the game’s progression. For successful positional rotations, tactical awareness is essential. The team’s overall game plan must be understood by all players, and they must also know how to maneuver in a way that won’t sabotage the defense of the opposition.
For instance, if the team employs a high-pressing strategy, players need to be aware of when to rotate positions to close down passing lanes and force turnovers in specific areas of the pitch.
- Communication and Coordination
Effective communication is vital for smooth positional rotations. Players should communicate their intentions and movements to their teammates to avoid confusion and prevent defensive gaps. Coordinated rotations can lead to seamless transitions, making it harder for opponents to anticipate the team’s next move. Clear and concise communication ensures that everyone is on the same page and can execute the rotations smoothly.
An example of communication and coordination during positional rotations can be seen when players use specific hand signals or verbal cues to indicate their intended movements and rotations to their teammates.
Examples of Positional rotations
In addition to basic positional rotations, advanced strategies can take team dynamics to the next level. Let’s explore some innovative approaches:
- Underlaps and overlaps
In the context of football, underlaps and overlaps refer to tactical movements made by players to create space and provide passing options for their teammates during an attacking play.
An underlap occurs when a player makes a diagonal or inward run towards the center of the pitch, moving behind or underneath a teammate who has the ball. This movement allows the player to receive a pass in a central position, often in a more advanced position, and potentially create a scoring opportunity. The underlapping player aims to exploit the space left by the teammate with the ball, who may have drawn the attention of defenders or created a diversion.
Conversely, an overlap involves a player making a run on the outside of a teammate who has the ball, typically a full-back or wing-back overlapping a winger or attacking midfielder. The overlapping player aims to stretch the opposition’s defense by moving into wider positions and providing an additional passing option. This tactic can create opportunities for crosses into the box or cut-back passes for teammates in central positions.
Both underlaps and overlaps are used to confuse the opposing defenders, create numerical advantages in specific areas of the pitch, and increase the options available to the team in possession of the ball. These tactics require good coordination, communication, and understanding between teammates to effectively exploit the spaces and create scoring opportunities.
- Numerical Overloading
Overloading involves concentrating multiple players in a specific area of the field to overwhelm the opposition’s defense. By creating numerical superiority, teams can penetrate defenses more easily and create goal-scoring opportunities. Overloading requires precise positioning and coordinated movement. Players need to time their runs and rotations effectively to create space and open up passing lanes.
For example, a team might overload the central midfield area by rotating a winger and a central midfielder into that space. This creates an overload, pulling the opposition’s defenders towards the center and creating space for wide players or fullbacks to exploit on the flanks.
- False Nine
The false nine strategy involves positioning a forward player in a deeper role, between the opponent’s midfield and defensive lines. This positioning confuses the opposition’s defenders, as they are unsure whether to track the forward or stay in their defensive positions. The false nine strategy can create space for other attackers and disrupt the opposing team’s defensive structure. The false nine needs to be comfortable dropping deep to link play and draw defenders out of position.
A famous example of the false nine strategy is Lionel Messi’s role at Barcelona. Messi often drops deep into midfield, drawing defenders out of position and creating space for his teammates to exploit.
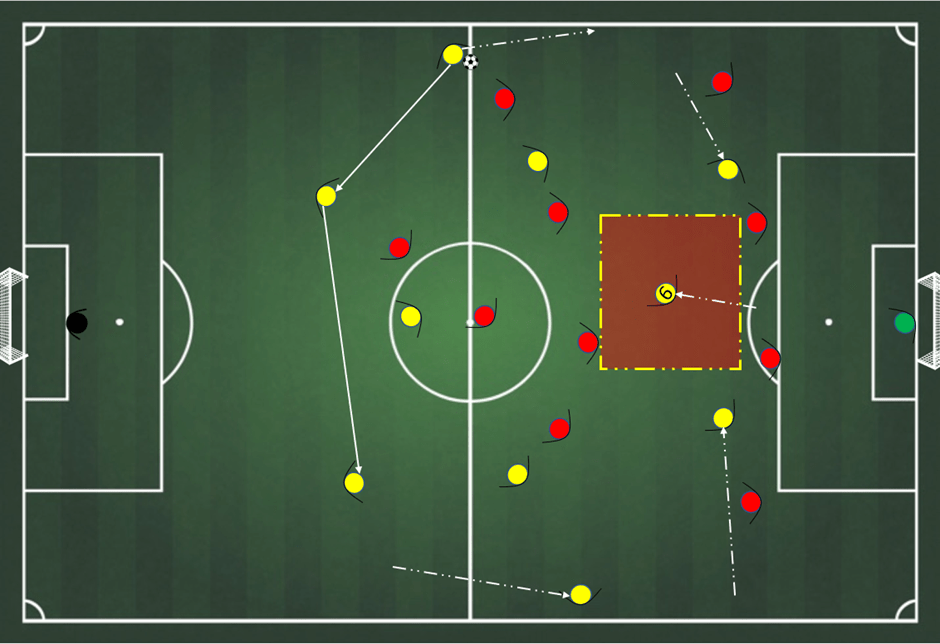
- Wide rotations
Fullbacks are typically responsible for both defensive duties and supporting the attack. By rotating fullbacks with wingers and inside midfielders, teams can create unpredictability and confusion for the opposing wingers and fullbacks. The rotations allow fullbacks to exploit spaces, provide additional attacking options, and contribute to the team’s overall fluidity. Fullbacks can overlap with wingers, switch flanks, or even make underlapping runs to create mismatches and overload specific areas of the field.
An example of rotating fullbacks can be seen when a team’s right-back overlaps with the right winger, creating an overload on that side of the pitch and providing an extra passing option or a crossing opportunity.
Read books to educate on Positional play and rotations
How to Train Positional Play – 15 Exercises

A practical guide on How to Train Guardiola’s Methodology
- Positional Play Methodology, also known as “Juego de Posicion,” is a revolutionary approach to football tactics that aim to create superiorities in specific areas of the pitch. This book “How to Train Positional Play – 15 Exercises” provides a comprehensive guide to understanding and implementing this methodology, offering 15 practical exercises for coaches and football enthusiasts. Written in a simple and informative manner, it sheds light on the key principles and concepts behind Positional Play.
- One notable aspect of this book is its emphasis on the influential coaches who have employed Positional Play throughout history. While Pep Guardiola is often associated with this style of play, the book recognizes the contributions of legendary coaches like Rinus Michels, Johan Cruyff, and Louis van Gaal, among others. It highlights their innovative concepts and techniques, allowing readers to appreciate the evolution of modern-day positional play.
- The author’s intention is to make Positional Play accessible to all coaches and football lovers. By explaining the fundamental principles and guidelines, this book equips readers with the necessary knowledge to implement Positional Play effectively. However, the focus remains on offering practical insights and training exercises rather than delving into theoretical complexities.
- The inclusion of 15 positional play exercises is a significant highlight of this book. These exercises serve as valuable tools for coaches to train their teams and develop a deep understanding of Positional Play. Each exercise is clearly explained, and the accompanying diagrams and illustrations further enhance comprehension. By following these exercises, readers can improve their tactical awareness and enhance their team’s performance on the pitch.
How to train positional rotations
Positional games and rondos are additional training methods that can enhance players’ understanding and execution of positional rotations. These exercises focus on improving players’ awareness, decision-making, and technical skills within specific positions. Here are a few examples:
- Passing patterns: Create two triangles inside a bigger rectangle space with two players positioned at each corner. Players must rotate positions within the triangle while maintaining ball possession and creating passing angles with the outside players. This drill emphasizes coordinated movements and quick decision-making, promoting effective positional rotations.
- Positional Game: Divide the team into smaller groups and assign specific positions to each group (e.g., defenders, midfielders, forwards). Play a possession-based game where players must maintain their positional roles and rotate positions intelligently to retain possession.
- Rondos: Rondos are small-sided games that emphasize quick passing, movement, and decision-making. Incorporate rondos into training sessions, ensuring players rotate positions frequently to develop their positional awareness and adaptability.
Positional games and rondos provide players with opportunities to apply positional rotations in dynamic and realistic game scenarios, enhancing their ability to execute these rotations effectively during matches.
Training positional rotations requires consistent practice, effective communication, and a deep understanding of the team’s tactics and objectives. By implementing tactical drills, communication exercises, match simulations, positional games, and rondos, coaches can equip their players with the skills necessary to execute positional rotations successfully.
Conclusion
Football positional rotations can enhance team relationships, offensive potential, and adaptability. Teams can triumph over competitors and perform well on the field by utilizing cutting-edge concepts and tactical rotations. Positional rotations can improve a team’s performance and provide a dynamic playing style if they are understood and used properly.
Please support us by hitting the like button on this prompt. This will encourage us to further improve this prompt to give you the best results.

