In this blog post, we will explore the superiorities in positional play in football. Football coaching is complex and requires teamwork, strategy, and skill. One methodology that can help a team to be successful is Positional Play.
Positional play is a tactical approach to football that emphasizes the use of space, teamwork, and player positioning to generate superiorities on the field.
Table of Contents
Disclosure: Please note that some of the links below area affiliate links and at no additional cost to you I will earn a commission. Know that i only recommend products services and brands I have personally used and stand behind. When you use one of my affiliate links, the company compensates me, which helps me run this blog and keep my in -depth content free of change for readers (like you). Read our disclosure for more info.
Why is important to create superiorities in Positional Play in football?
One of the most significant elements for a team playing a positional game is “superiorities“. Creating superiorities in positional play football is important because it can give a team a significant advantage over their opponents. By generating numerical, positional, qualitative, and socio-affective superiority, a football manager can create for his team more passing options, control the tempo of the game, and ultimately create better quality chances.
Moreover, establishing superiorities can assist a team in destroying a well-organized defense and opening up gaps in the opposition’s formation. More 1 v 1 opportunities or possibilities for shots on goal may result from this, boosting the possibility of scoring.
Establishing superiorities can also help a team defend more successfully. For example, when a team uses a numerical superiority in a specific area in the pitch, in case of losing the ball it’s much easier to apply immediate pressure to recover it back.
In past decades, the influence of Total Football, pioneered by Rinus Michels, reshaped the tactical landscape of the sport, leaving a lasting impact on clubs like FC Barcelona and Ajax.
This revolutionary approach emphasized fluidity, allowing players to interchange positions, blurring the lines between defender, midfielder, and forward roles. Total Football laid the foundation for concepts like juego de posición, which further refined positional principles and spatial awareness. Barcelona, under Johan Cruyff and later Pep Guardiola, applied these ideas not only at the senior level but also in youth football, creating a pipeline of talent grounded in this philosophy.
Bayern Munich, after the appointment of Guardiola as their manager and Germany integrated similar methods, achieving success at both club and international levels, including World Cup triumphs for key players. The role of the defensive midfielder became pivotal, balancing defensive duties with initiating attacks, reflecting the enduring legacy of Michels’ visionary approach across generations.
In recent years, Premier League teams have increasingly relied on superiorities in various aspects of the football game to gain a competitive edge. Managers like Jürgen Klopp and Roberto De Zerbi, former coach of Brighton, have emphasized possession play and positional discipline to dominate opponents and control matches.
By focusing on ball progression and precise player rotations, teams can break down defensive setups and create more opportunities for offensive players. This playing style allows key figures like Kyle Walker to seamlessly transition between defensive and attacking roles, enhancing fluidity and adaptability.
Superiorities in possession and tactical awareness not only improve overall team performance but also expose weaknesses in the opposition, ultimately contributing to consistent success in the Premier League.
Developing positional play superiorities is essential to succeeding on the field overall. As a result, more wins are achieved since teams can manage the action, control possession, and generate more scoring possibilities.
Which principles are important to create superiorities to play a positional play in football?
In football, “superiority” describe circumstances in which one team enjoys a kind of advantage over the other. This can be done through a variety of strategies, such as overloading certain areas of the field, focusing on certain players, or taking advantage of defensive weaknesses.
In positional play in football, superiorities are generated by using the following principles:
- Maintaining an organized structure:
- An organized structure is essential for a team to generate superiorities. This means that players need to be positioned in a way that creates passing lanes and allows for quick transitions between attack and defense.
- The different names of positions (WG, FB, AM etc.) loses their actual meaning and what it matters is the area in the pitch that they occupy. So, the term “Wide position” is more important than the term “Winger“.
- A team that maintains an organized structure is better able to control the flow of the game and create opportunities to score.
- Building player relationships:
- In order to generate superiorities, players need to work together effectively. This means building relationships based on trust, communication, and understanding.
- In positional play football, developing player relationships is crucial because it encourages connectivity and fluidity in a team’s movements.
- Players that engage in positional play must continually modify their positions and act quickly in response to the movements of their teammates and opponents. Players that have deep bonds with one another are better able to read each other’s body language and make rapid, accurate passes without the use of words.
- Building relationships off the field can also result in improved team morale and better performances on the field by improving communication and understanding among colleagues.
- Exploiting space:
- Space is a valuable resource in football, and teams that are able to use it effectively can generate superiorities.
- In positional play football, creating an exploit space is essential for a team to compromise the defense of the opposition and generate scoring opportunities.
- A team can drag the opposing defense out of position and create holes that can be exploited with well-timed passes or runs by establishing an exploit space.
- This means creating and exploiting spaces in the opposition’s defense, as well as maintaining a compact shape in defense to limit the opponent’s space to play.
The above example is taken out from one of the best tactical books I have read on Guardiola’s Manchester City “PEP GUARDIOLA ATTACKING TACTICS – TACTICAL ANALYSIS AND SESSIONS FROM MANCHESTER CITY’S 4-3-3“.
Here City creates and exploits the space on the weak side by having the winger keeping position on the right side flank.
- Creating overloads:
- Creating overloads in certain areas of the pitch can help a team to generate superiorities.
- This means having more players in a certain area of the pitch than the opposition, which can lead to more passing options and opportunities to score.
Teams can create superiorities in a variety of ways by applying these ideas. For instance, they might isolate specific players to create one-on-one situations in midfield, employ rapid passing to create overloads there or rotate players into different positions to throw the opposition’s defense off.
Which are the 4 types of superiorities of positional play in football?
In football, there are four types of superiorities that can be generated through positional play. These superiorities refer to situations where a team has a numerical or positional advantage over its opponents. The four types of superiorities are:
- Numerical superiority:
- This refers to situations where a team has more players in a specific area of the pitch than their opponents. This can be achieved by creating overloads or by drawing players out of position.
- For example, a team might drop more players backward than the defenders can mark, creating a numerical advantage in the defensive third of the pitch. This can make it easier for the attacking team to break the opposition’s first line of pressure.
- Numerical superiority can provide more passing options, allowing the team to dominate possession and control the tempo of the game.
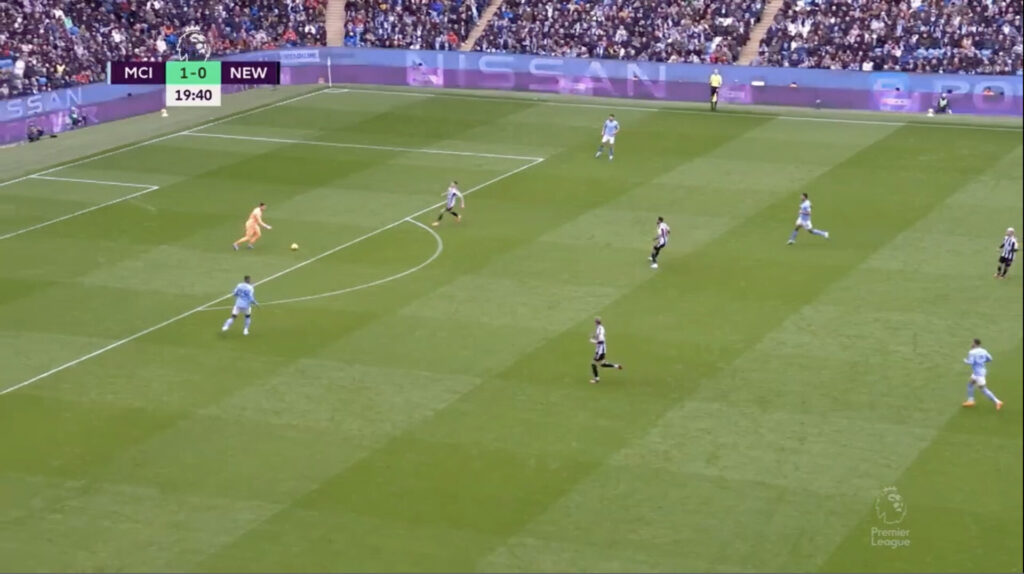

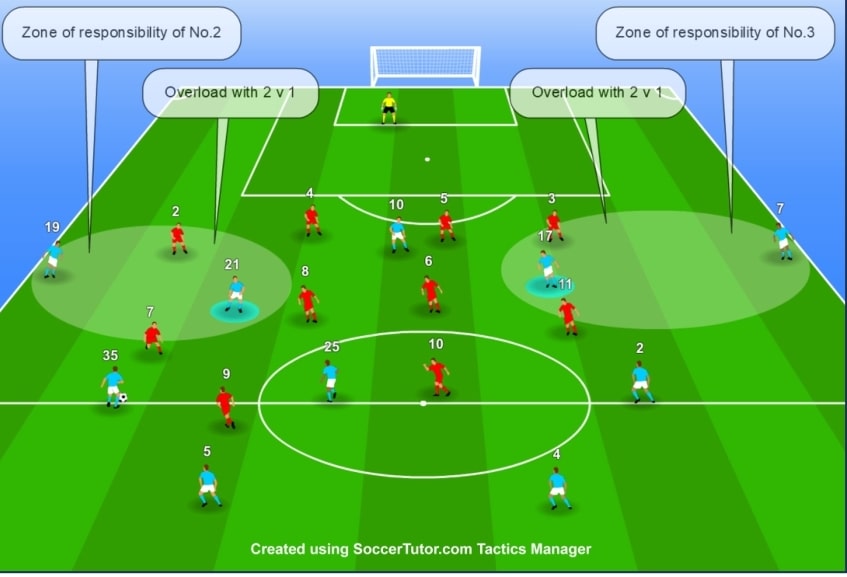
Example of 4 + GK vs 4 in Manchester City build up. The superiority is created with the GK which creates a free man – the weak side center back
Example of 4 + GK vs 3 in Barcelona build up. The superiority is created with the GK + 1 player which creates a free man – the dropping attacking midfielder
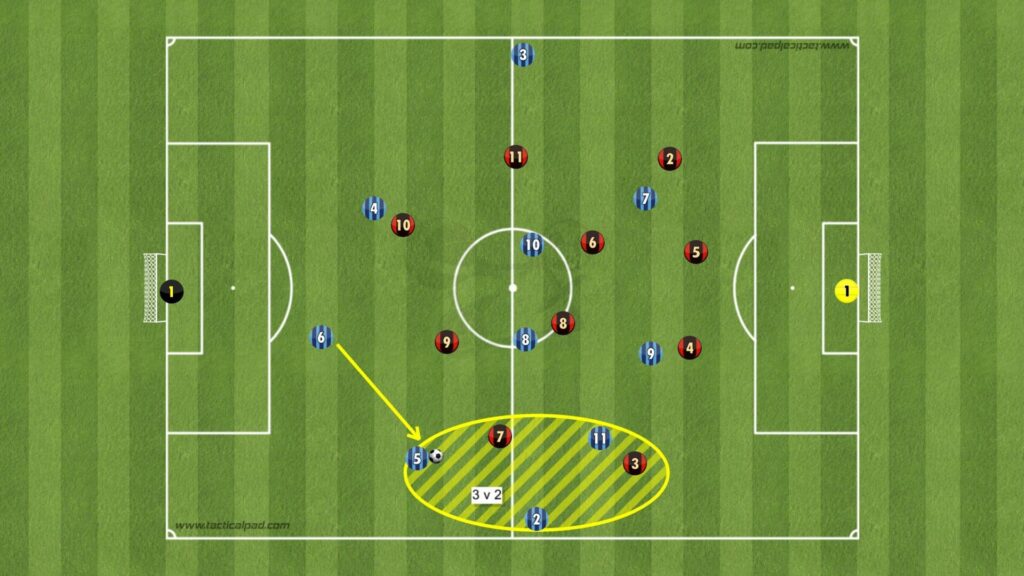
In the above picture, the numerical overload is done to the right side. The example above is extracted from the book “Positional Play in Modern Football“
- Positional superiority:
- Positional superiority in positional play in football refers to a situation where a team is able to control the game by having players in favorable positions on the pitch. This can be achieved through effective positioning and movement of players to create passing options, support teammates, and exploit the opposition’s weaknesses.
- More usual is to stretch the opposition’s defense and exploit gaps in their formation. a team can create positional superiority by exploiting the gaps in the opposition’s formation. Playing between the lines is the result of positional superiority.
- Players occupying half-spaces in probably the most well-known situation of positional play since the opposing FB have a challenge to decide which player should mark, the Attacking midfielder in the half-space or the wide winger on the side line.
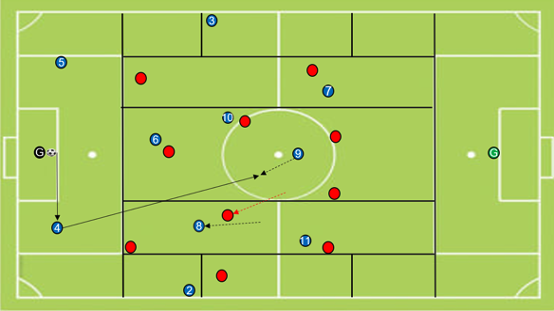
An example of Positional Quality from the book “15 Exercises to train Positional Play“
- Socio-affective superiority
- Socio-Affective superiority describes a condition where a team is able to demonstrate strong bonds and open lines of communication among its players. Building trust, empathy, and teamwork among teammates are all facets of this kind of superiority that are centered on the social and emotional sides of the game.
- Players in socio-affective superiority come to understand each other’s advantages, disadvantages, and playing preferences. This enables them to assist one another on the field, make wise choices, and cooperate toward a common objective.
- Team’s that have players who play for many years together or coming from the same academy and were trained under the same philosophy is much easier to create a socio-affective superiority. A classic example is Guardiola’s Barcelona of 2008 – 2012.
- Qualitative superiority:
- This refers to situations where a team has a higher level of technical or physical ability than their opponents. This can be achieved through individual skill, fitness, or tactics.
- Qualitative superiority can make it easier for a team to dominate possession and create chances, and can also make it more difficult for the opposition to create their own superiorities.
- Player’s like Messi, Salah, Foden and Kvaratskhelia can be so dangerous in 1 v1 or even against more opponents.
By understanding these 4 types of superiorities and how to generate them through positional play, coaches and players can develop a strategic approach to football that maximizes their chances of success. By creating and exploiting superiorities, teams can gain a significant advantage over their opponents and ultimately achieve their goals on the pitch.
Conclusion
In conclusion, positional play in football is a tactical approach to football that emphasizes the use of space, teamwork, and player positioning to generate superiorities. By maintaining an organized structure, building player relationships, exploiting space, and creating overloads, teams can create opportunities to score and control the flow of the game.
By understanding these principles, coaches, and players can develop a strategic approach to football that maximizes their chances of success.

